Enable scalable Redis Query Engine in Redis Enterprise
Enable the scalable Redis Query Engine in Redis Enterprise to increase the performance of queries.
Redis Query Engine is a capability intended to increase the performance of queries, including vector search. When enabled, it allows you to increase a database's compute capacity and throughput by allocating more virtual CPUs per shard in addition to horizontal scaling with more shards. This document describes how to configure the Redis Query Engine.
Prerequisites
Redis Query Engine requires a cluster running Redis Enterprise Software version 7.4.2-54 or later.
If you do not have a cluster that supports Redis Query Engine, install Redis Enterprise Software version 7.4.2-54 or later on a new cluster, or upgrade an existing cluster.
Sizing
-
Calculate the hardware requirements for your Redis database:
-
Use the hardware requirements documentation to derive the overall cluster architecture.
-
Calculate the RAM requirements using the Index Size Calculator. The total RAM required is the sum of the dataset and index sizes.
-
-
Determine the scaling factor you want and the required number of CPUs. Unused CPUs, above the 20% necessary for Redis, can be used for the scalable Redis Query Engine.
-
Create a new Redis database with the number of CPUs configured for the scalable Redis Query Engine.
Calculate scaling factor
CPUs for Redis Query Engine
Vertical scaling of the Redis Query Engine is achieved by provisioning additional CPUs for the search module. At least 20% of the available CPUs must be reserved for Redis internal processing. Use the following formula to define the maximum number of CPUs that can be allocated to search.
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| CPUs per node | x |
| Redis internals | 20% |
| Available CPUs for Redis Query Engine | floor(0.8 * x) |
Scale factor versus CPUs
The following table shows the number of CPUs required for each scale factor. This calculation is sensitive to how the search index and queries are defined. Certain scenarios might yield less throughput than the ratios in the following table.
| Scale factor | Minimum CPUs required for Redis Query Engine |
|---|---|
| None (default) | 1 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 6 |
| 6 | 9 |
| 8 | 12 |
| 10 | 15 |
| 12 | 18 |
| 14 | 21 |
| 16 | 24 |
Example scale factor calculation
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| CPUs per node | 8 |
| Available CPUs | floor(0.8 * 8)=6 |
| Scale factor | 4x |
| Minimum CPUs required for scale factor | 6 |
Enable scalable Redis Query Engine
To enable the scalable Redis Query Engine in Redis Enterprise, use the REST API to create a new database or update an existing database.
Create new database
To create a database with the scalable Redis Query Engine enabled, use the create database REST API endpoint with a BDB object that includes the following parameters:
{
"sched_policy": "mnp",
"conns": 32,
"module_list": [{
"module_name": "search",
"module_args": "MT_MODE MT_MODE_FULL WORKER_THREADS <NUMBER_OF_CPUS>"
}]
}
See Calculate scaling factor to determine the value to use for <NUMBER_OF_CPUS>.
Example REST API request for a new database
The following JSON is an example request body used to create a new database with the scalable Redis Query Engine enabled:
{
"name": "scalable-search-db",
"type": "redis",
"memory_size": 10000000,
"port": 13000,
"authentication_redis_pass": "<your default db pwd>",
"proxy_policy": "all-master-shards",
"sched_policy": "mnp",
"conns": 32,
"sharding": true,
"shards_count": 3,
"shards_placement": "sparse",
"shard_key_regex": [{"regex": ".*\\{(?<tag>.*)\\}.*"}, {"regex": "(?<tag>.*)"}],
"replication": false,
"module_list": [{
"module_name": "search",
"module_args": "MT_MODE MT_MODE_FULL WORKER_THREADS 6"
}]
}
The following cURL request creates a new database from the JSON example:
curl -k -u "<user>:<password>" https://<host>:9443/v1/bdbs -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d @scalable-search-db.json
Update existing database
To enable the scalable Redis Query Engine for an existing database, use the following REST API requests:
-
Update database configuration to modify the DMC proxy.
-
Upgrade module to set the search module’s scaling factor.
The following example script uses both endpoints to configure a 4x scale factor:
#!/bin/bash
export DB_ID=1
export CPU=6
export MODULE_ID=`curl -s -k -u "<user>:<password>" https://<host>:9443/v1/bdbs/$DB_ID | jq '.module_list[] | select(.module_name=="search").module_id' | tr -d '"'`
curl -o /dev/null -s -k -u "<user>:<password>" -X PUT https://<host>:9443/v1/bdbs/$DB_ID -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{
"sched_policy": "mnp",
"conns": 32
}'
sleep 1
curl -o /dev/null -s -k -u "<user>:<password>" https://<host>:9443/v1/bdbs/$DB_ID/modules/upgrade -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{
"modules": [
{
"module_name": "search",
"new_module_args": "MT_MODE MT_MODE_FULL WORKER_THREADS '$CPU'",
"current_module": "'$MODULE_ID'",
"new_module": "'$MODULE_ID'"
}
]
}'
Monitoring Redis Query Engine
To monitor a database with the scalable Redis Query Engine enabled:
-
Integrate your Redis Enterprise deployment with Prometheus. See Prometheus and Grafana with Redis Enterprise for instructions.
-
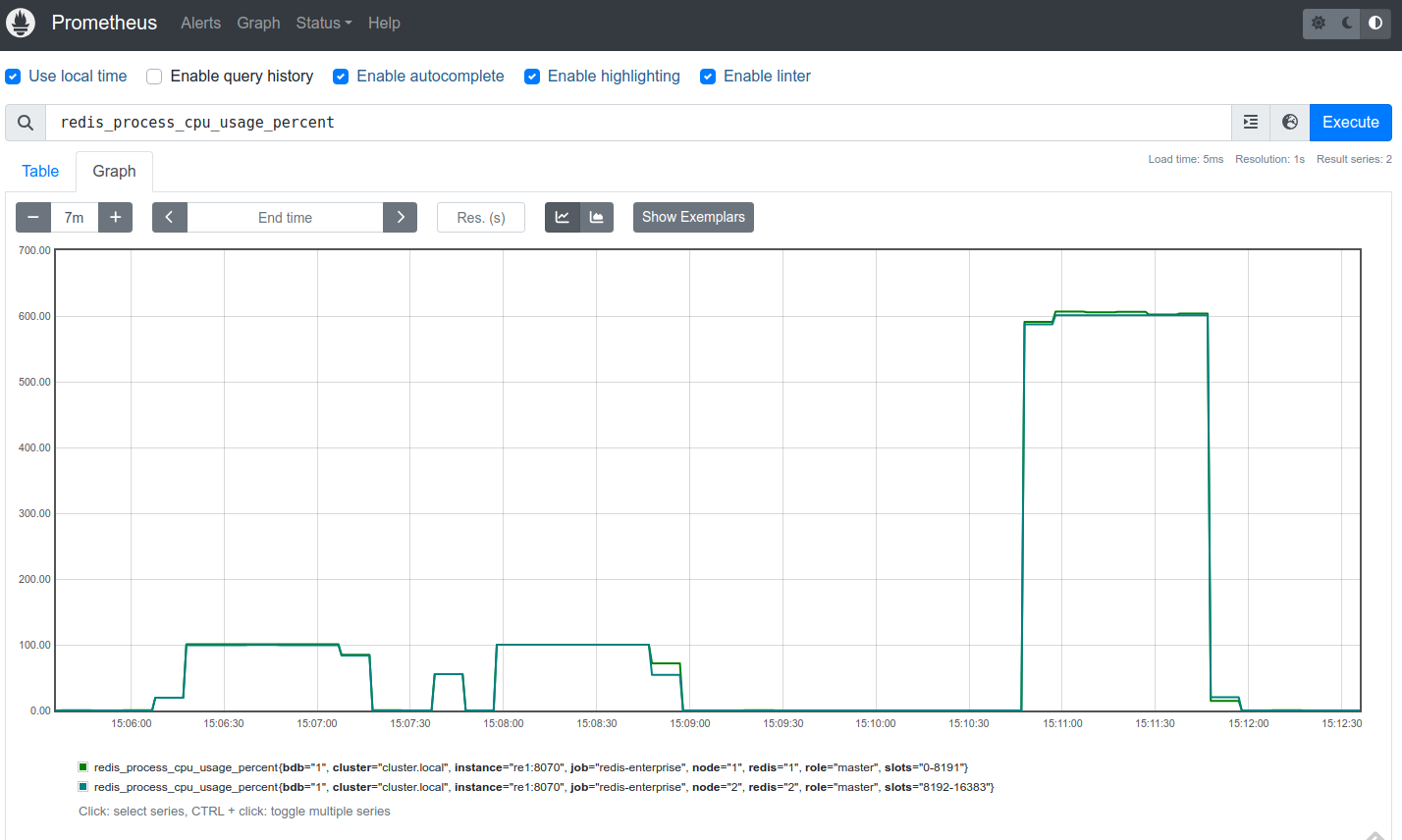
Monitor the
redis_process_cpu_usage_percentshard metric.The following Prometheus UI screenshot shows
redis_process_cpu_usage_percentspikes for a database with two shards:-
1st 100% spike:
memtier_benchmarksearch test at the default scale factor (1 CPU per shard for search). -
2nd 100% spike: reconfiguration and shard restart for a 4x scale factor.
-
3rd 600% spike:
memtier_benchmarksearch test with threading at a 4x scale factor (6 CPUs per shard).
-